Terraform如何调用Ansible配置虚拟机资源
Terraform(https://www.terraform.io/)是一款开源的基础架构即代码(Infrastructure As Code - IAC)工具,通过代码来构建和变更基础架构,并且能够管理变更的版本。Terraform在构建出虚拟机资源后,往往会调用与其关联的provisoner来配置虚拟机资源,比如变更某个系统配置,设置环境变量或者部署某个应用,但是Terraform目前并没有提供开箱即用的支持Ansible的provisioner(也许随着版本的升级,会提供)。本文基于vSphere数据中心和Ubuntu系统实现一种Terraform调用Ansible配置虚拟机资源的方法。
Terraform架构简介
为了方便后续步骤的理解,在这里对Terraform及其相关组件做一简单介绍。这是Terraform的架构图: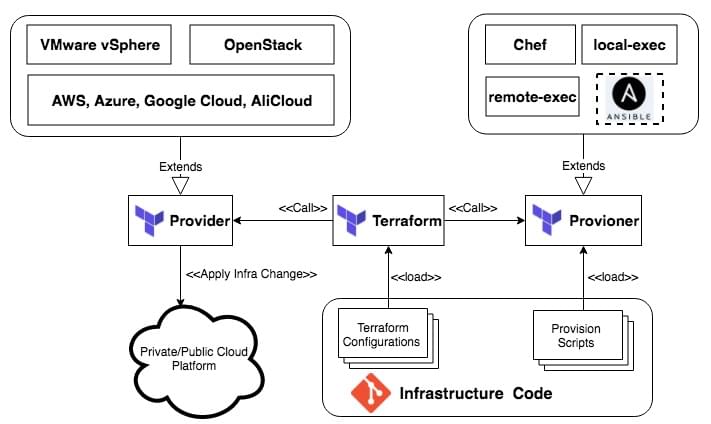
Terraform调用不同云平台(公有或私有)的“Provider”创建和编排基础架构资源,调用不同的“Provisioner”配置新生成的资源。并不是所有的资源都支持“Provisioner”,可以参考对应资源的帮助文档来了解是否支持。基本上,虚拟机资源,比如ECS, EC2等,都支持调用“Provisioner”去配置。
实现思路
组合利用Terraform现有的Provisioner为新创建的虚拟机生成动态的Ansible资源文件,加入到Ansible当前资源文件夹中(Ansible在执行时会合并当前资源文件加下的所有资源文件),最后基于动态资源执行Ansible脚本配置新创建的虚拟机。
具体实现
以自动创建一台虚拟机资源并安装和配置Artifactory软件为例,下图是Terraform+Ansible的代码结构:
.
├── ansible
│ ├── handlers
│ ├── inventory
│ │ ├── devops
│ │ │ ├── group_vars
│ │ │ ├── host_vars
│ │ │ └── hosts
│ │ └── devops-disconf
│ │ └── hosts
│ ├── roles
│ ├── templates
│ │ ├── artifactory
│ │ │ └── hosts.temp.j2
│ ├── configure-ansible-node.sh
│ ├── ansible.cfg
│ ├── terraform-ansible-inventory.yaml
│ ├── artifactory.yaml
├── iac
│ └── cicd
│ ├── vsphere_virtual_machine_art1.tf
Artifactory是一款统一制品管理工具,支持多种标准的软件包格式:Maven(Gradle),Nuget,NPM,Bower,CocoaPods,Docker,Debian,RPM…,也支持自定义存储格式。Artifactory是构建CI/CD流程必不可少的一个工具。
ansible目录
这个目录是典型的Ansible工程目录,有handlers,inventory,roles,templates,ansible.cfg,*.yaml(Ansible playbook)。
ansible.cfg
设置缺省的资源文件夹,比如:
1
2[defaults]
inventory = ./inventory/devops在资源文件夹中,一般会有一个缺省的资源文件hosts,另外还有组变量文件和主机变量文件。
configure-ansible-node.sh
Shell脚本,用来在新创建的虚拟机中(Ubuntu)安装Python,以便将这台虚拟机配置成Ansible的管理节点。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
py_version=2.7.12-1~16.04
if [ -f /var/lib/apt/lists/lock ]
then
rm -f /var/lib/apt/lists/lock
fi
result=$(dpkg-query -W python | awk '{print $2}')
if [ -z "${result}" ]
then
echo "Installing python=${py_version}"
else
echo "python was already installed!"
exit 0
fi
export http_proxy=http://xxxx
export https_proxy=${http_proxy}
cat > /etc/apt/apt.conf.d/apt-temp.conf <<EOF
Acquire::http::Proxy "${http_proxy}";
Acquire::https::Proxy "${http_proxy}";
Acquire::ftp::Proxy "${http_proxy}";
EOF
apt-get update
apt-get -y --no-upgrade install python=${py_version}
curl https://bootstrap.pypa.io/get-pip.py | python
pip install -U pip
rm -f /etc/apt/apt.conf.d/apt-temp.conf如果代码是运行在防火墙后面,比如在公司的网络中,需要line 19 - line 26的代码配置apt代理。
terraform-ansible-inventory.yaml
Ansible脚本,用来生成当前虚拟机的动态资源文件:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11- name: Create temp inventory file
hosts: "{{ host | default('localhost') }}"
vars:
host_name: default-temp
host_ip: xxx.xxx.xxx.xxx
host_user: xxx
host_password: xxx
tasks:
- name: Create temp inventory file
template: src=artifactory/hosts.temp.j2 dest=inventory/devops/{{host_name}} mode=644
delegate_to: localhost本地执行这个Ansible脚本从以下模板(hosts.temp.j2)实例化出Ansible的资源文件。
1
2
3
4{{host_name}} ansible_host={{host_ip}} ansible_user={{host_user}} ansible_password={{host_password}} ansible_ssh_common_args='-o StrictHostKeyChecking=no'
[packer_node]
{{host_name}}因为在动态资源文件中使用了用户名和密码的方式访问虚拟机。需要在Ansible控制机上安装sshpass。
iac目录
这个目录用来存放Terraform配置文件。
vsphere_virtual_machine_art1.tf
Terraform配置文件,在vsphere中从某个虚拟机模板克隆创建一台新的虚拟机资源。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55provider "vsphere" {
vsphere_server = "xxx.xxx.xxx.xxx"
user = "..."
password = "..."
allow_unverified_ssl = true
}
resource "vsphere_virtual_machine" "art1" {
...
clone {
template_uuid = "..."
...
}
provisioner "file" {
source = "../../ansible/configure-ansible-node.sh"
destination = "/tmp/configure-ansible-node.sh"
connection {
type = "ssh"
user = "..."
password = "..."
agent = false
}
}
provisioner "remote-exec" {
inline = ["chmod a+x /tmp/configure-ansible-node.sh",
"/tmp/configure-ansible-node.sh",
"rm -f /tmp/configure-ansible-node.sh"]
connection {
type = "ssh"
user = "..."
password = "..."
agent = false
}
}
provisioner "local-exec" {
command = "ansible-playbook -e host_name=default_art1 -e host_ip=${vsphere_virtual_machine.art1.default_ip_address} terraform-ansible-inventory.yaml",
working_dir = "../../ansible"
}
provisioner "local-exec" {
command = "ansible-playbook -e host=default_art1 artifactory.yaml",
working_dir = "../../ansible"
}
provisioner "local-exec" {
command = "rm -f inventory/devops/default_art1",
working_dir = "../../ansible"
}
}line16 - line26:利用Terraform的”file“provisioner上传安装Python的Shell脚本
line28 - line39:利用Terraform的”remote-exec“provisioner执行安装Python的Shell脚本
line41 - line44:获取新生成的虚拟机IP地址,利用Terraform的”local-exec“provisioner本地执行“terraform-ansible-inventory.yaml”生成Ansible的动态资源文件
line46 - line49:利用Terraform的”local-exec“provisioner基于Ansible的动态资源文件执行Ansible脚本完成应用的部署和配置
line51 - line54:利用Terraform的”local-exec“provisioner执行Shell命令删除动态资源文件
结束
这个方法同样也适用于在公有云平台上创建虚拟机实例并调用Ansible脚本完成配置,但需要为虚拟机实例绑定一个动态的公网IP地址。
Terraform如何调用Ansible配置虚拟机资源